VACCINE VIAL MONITOR (VVM)
What is vaccine vial monitor?
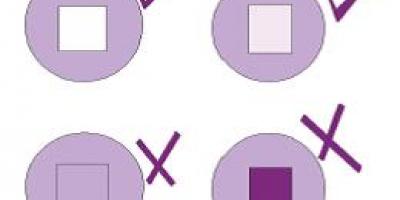
VVM is a small label stuck on the vial of a vaccine which changes color as the vaccine vial is exposed to heat.
The color of the VVM central square indicates if the vaccine is safe for use or not. It is a small light purple circle with a white square in the center. The square remains white if there is no exposure to heat. With heat exposure the square begins to darken. It registers the cumulative heat exposure over time.