DPT AND TT VACCINES
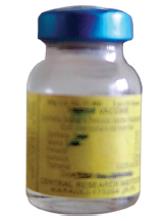
Diphtheria, Pertussis, and Tetanus(DPT; Triple Antigen)
Identification features
The vaccine is available in small glass bottles mostly having a blue metallic cover.
Type of vaccine
Killed (diphtheria toxoid, tetanus toxoid, and killed bacteria of pertussis)
Site of injection
Anterolateral aspect of LEFT mid-thigh





