Currently, there are three types of JE vaccines in use:
1. The mouse brain-derived inactivated (Killed) vaccine.
2. The cell culture-derived inactivated (Killed) vaccine.
3. The cell culture-derived live, attenuated vaccine using SA 14-14-2 strain of JE virus.
Under the National program, the live attenuated (SA 14-14-2), cell culture-derived vaccine is used in India. It is presently manufactured in P. R. China. It is imported from there for use in India.
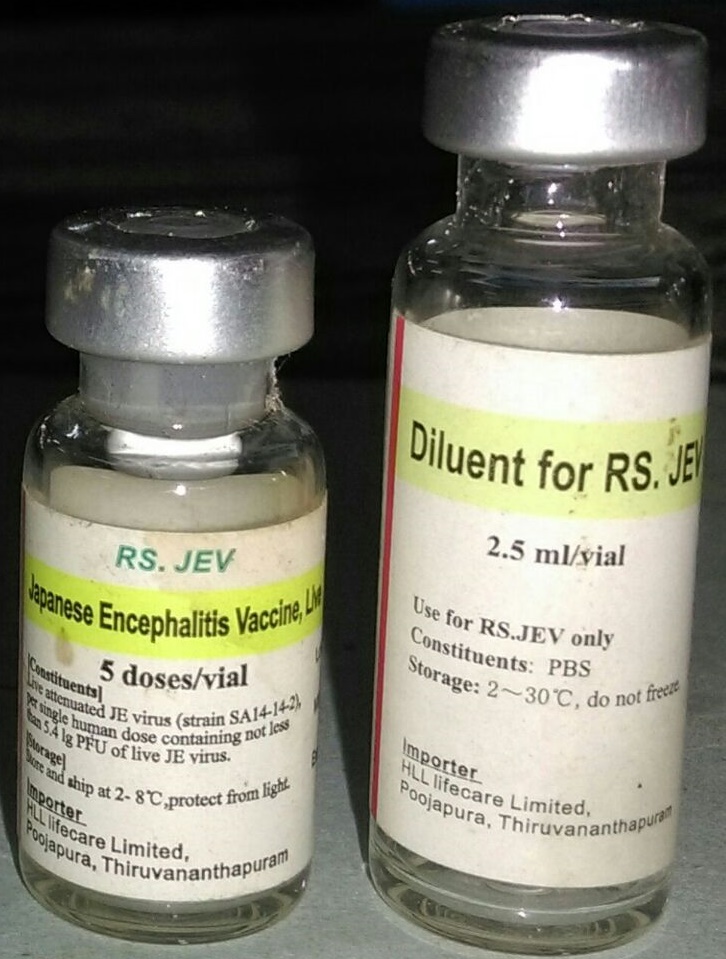
Identification features
The bottle contains milky white caked powder.
The label mentions that the vaccine is manufactured in China.
Type of vaccine
Live
Route of administration
Subcutaneous
Dose
0.5 mL
Site
Left upper arm
Whether part of NIS?
Included in the immunization schedule of select 83 JE endemic districts of Indian states
Schedule under NIS
Two doses of JE vaccine are administered in all JE endemic districts of the country.
1. The first dose is given at the age of 9–12months along with the first dose of measles vaccine and
2. The second dose is given at the age of 16 – 24 months along with DPT and OPV booster dose and measles second dose.
Diluent
Sterile phosphate buffered saline (PBS). The diluent supplied along with the vaccine by the manufacturer ONLY should be used.
Strain of JE virus used
Live, attenuated SA 14-14-2 strain of JE virus
Storage
• +2°C to +8°C
• Protect from light
• Diluents to be stored at +2°C to +8°C WHO
• Diluent must not be frozen
• Reconstitute only one vial of JE vaccine at one time and use vaccine within 6 hours of reconstitution
Side effects
• Transient fever
• Rash
• Irritability
• Local reactions such as injection site induration and tenderness
Contraindication
• Person with fever
• Acute infectious disease
• Active untreated tuberculosis
• Cardiac, liver, and kidney problems
• Pregnancy
• Allergy and convulsion
• Person treated with any immunosuppressive therapy
• Person with a proven or suspected hypersensitivity to kanamycin or gentamicin
• Person with a history of immunization with any other live, attenuated virus vaccine within 1 monthWHO website
Mild illness like URI is not a contraindication to JE vaccine
Protective efficacy
98–99%
Protective duration
Lifelong
Is ‘open vial policy’ applicable to JE vaccine?
No
Which strategy is being used for improving coverage with JE vaccine in India?
JE vaccine was introduced in 112 endemic districts in campaign mode from 2006-10 and has now been incorporated under the Routine Immunisation Programme of the endemic districts.
Which mosquitoes act as vectors of Japanese encephalitis?
Female culex mosquito
Name four Indian states which have districts endemic for Japanese encephalitis.
• Uttar Pradesh
• Assam
• West Bengal
• Karnataka
References:
Immunization standards. WHO website Available at: http://www.who.int/immunization_standards/vaccine_quality/pq271_jev_5dos... accessed on 7th November 2017
JE vaccines, health worker training materials, WHO website. Available at: http://www.who.int/immunization/diseases/japanese_encephalitis/training-... accessed on 7th November 2017
SA 14-14-2 LIVE JAPANESE ENCEPHALITIS (JE) VACCINE, Path website. Available at: https://www.path.org/publications/files/SA14142-fact-sheet-1013.pdf accessed on 7th November 2017
Universal Immunization Program, NIHFW website. Available at: https://www.nhp.gov.in/universal-immunization-programme-uip_pg accessed on 8th November 2017
National Immunization Schedule in India; 2017: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/national-immunization-schedule-india-2017
Rotavirus vaccine: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/rotavirus-vaccine
Pentavalent vaccine: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/pentavalent-vaccine
BACILLE CALMETTE GUERIN (BCG) VACCINE: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/bacille-calmette-guerin-bcg-vaccine
IPV (INACTIVATED POLIOVIRUS VACCINE): http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/ipv-inactivated-poliovirus-vaccine
DT & TT Vaccines: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/dpt-and-tt-vaccines
Oral Polio Vaccines (OPV): http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/oral-polio-vaccines-opv
Measles Containing Vaccines (MCV): http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/measles-containing-vaccines-mcv
HEPATITIS B VACCINE: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/hepatitis-b-vaccine
JAPANESE ENCEPHALITIS (JE) VACCINE: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/japanese-encephalitis-je-vaccine
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV): http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/pneumococcal-conjugate-vaccine-pcv
RABIES VACCINE: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/rabies-vaccine
CONCENTRATED VITAMIN A SOLUTION: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/concentrated-vitamin-solution
VACCINE VIAL MONITOR (VVM): http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/vaccine-vial-monitor-vvm
Adverse event following immunization (AEFI): http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/adverse-event-following-immunization-aefi
