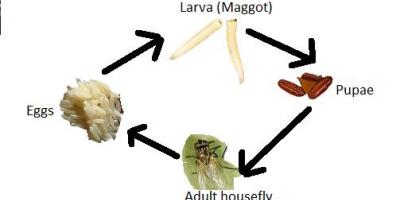
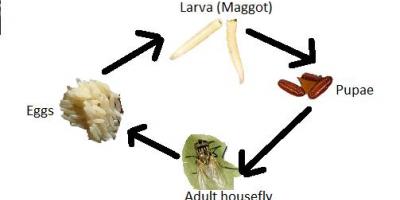
Concept of the “Consumption Unit”
When the food intake of a community or a group of people is to be measured, the practical problem that arises is that the group is constituted by individuals of various ages and sex groups. Each group has a different set of such groups.
To resolve this issue, it is usual to assess the needs of women and children in terms of those of the average man by applying appropriate coefficients of calorie consumption suggested for practical nutrition work in India.