Components of Monkeypox Case Management
1. Patient isolation
2. Protection of vulnerable skin and mucous membranes
3. Rehydration and maintain nutrition
4. Symptom relief
5. Watching out for and managing the complications
Patient Isolation
Isolation of the patient should be either in an isolation room of the hospital if needed or at home in a separate room with independent ventilation
Patient should wear a triple layer mask as large respiratory droplets are a major route of transmitting the infection
Skin lesions should be covered to the greatest possible extent (e.g. long sleeves, long pants) to minimize risk of contact with others
Isolation to be continued until all lesions have resolved and scabs have completely fallen off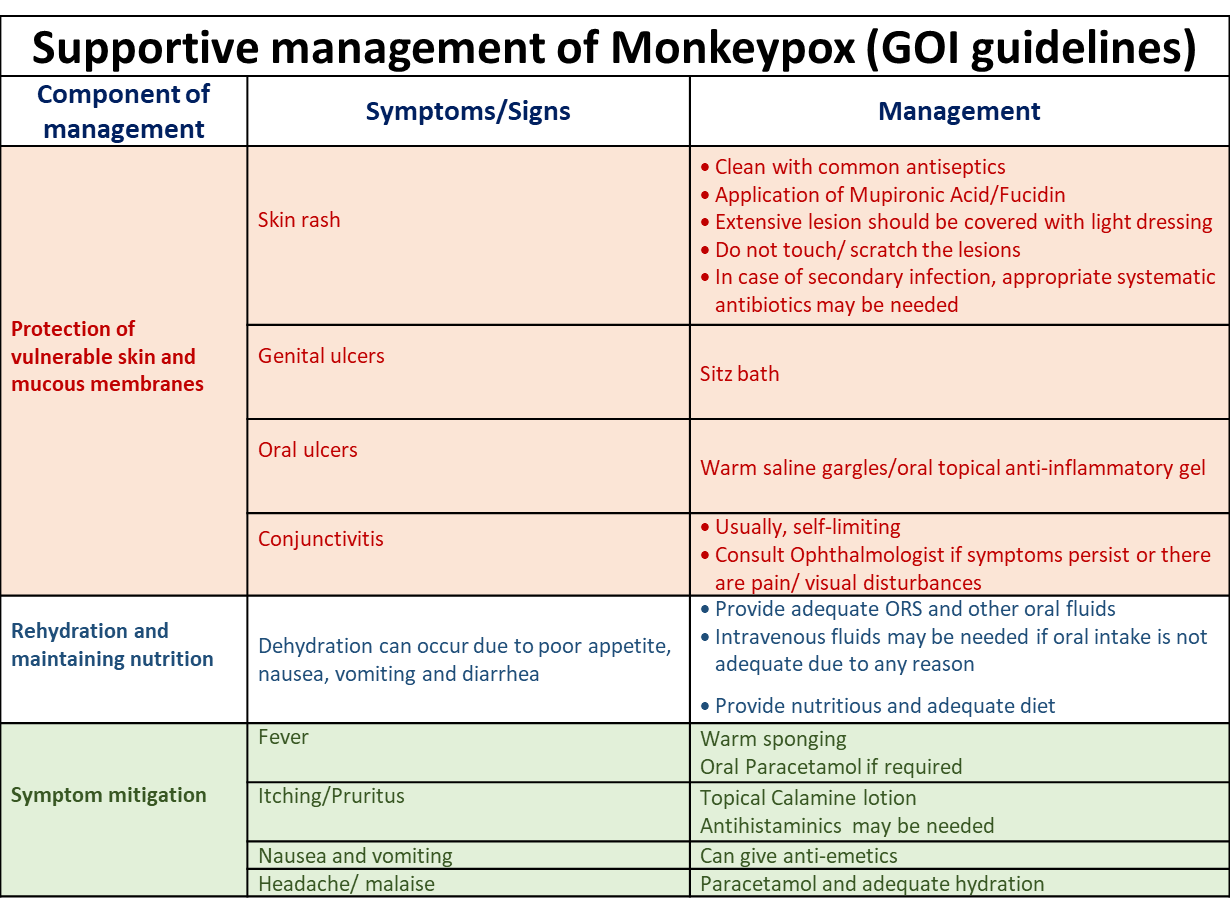
Watching out for and managing the complications
The patient should closely monitor for the appearance of any of the following symptoms during the period of isolation:
• Pain in eye or blurring of vision
• Shortness of breath, chest pain, difficulty in breathing
• Altered consciousness, seizure
• Decrease in urine output
• Poor oral intake
• Lethargy
In case any of the above symptoms appear, the patient should immediately contact nearby healthcare facility/ specialist.
Infection Prevention and Control at home
Patients who do not require hospitalization may be managed at home taking following preventive measures:
• Patients should be isolated in a room or area separate from other family members. Healthy household members should limit contact with the patient.
• Patients should not leave the home except for medical care.
• No visitors should be allowed at home.
• Patients, especially those who have respiratory symptoms (e.g., cough, shortness of breath, sore throat) should wear a surgical mask. If this is not feasible, other household members should consider wearing a surgical mask when in the presence of the patient.
• Disposable gloves should be worn for direct contact with lesions and disposed of after use. • Skin lesions should be covered to the best extent possible (e.g., long sleeves, long pants) to minimize risk of contact with others.
• Contain and dispose of contaminated waste (such as dressings and bandages) in the Biomedical waste disposable bag Do not dispose of waste in landfills or dumps.
• Proper hand washing with soap and water (or use of an alcohol-based hand rub) should be performed by the patient and other household members after touching lesion material, clothing, linens, or environmental surfaces that may have had contact with lesion material.
• Laundry (e.g., bedding, towels, clothing) may be washed with warm water and detergent;
1. Care should be used when handling soiled laundry to avoid direct contact with contaminated material.
2. Soiled laundry should not be shaken or otherwise handled in a manner that may disperse infectious particles.
• Dishes and other eating utensils should not be shared. Soiled dishes and eating utensils should be washed with warm water and dish washing soap.
• Contaminated surfaces should be cleaned and disinfected. Standard household cleaning/disinfectants may be used in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
• Pets and domestic animals should be excluded from the patient’s environment.
Duration of Isolation Procedures
Affected individuals should avoid close contact with immunocompromised persons and pregnant women until all crusts are gone. Isolation precautions should be continued until all lesions have resolved and a fresh layer of skin has formed.
Reference:
GOI, MoHFW, 2022. Guidelines for Management of Monkeypox Disease. Available at: https://main.mohfw.gov.in/sites/default/files/Guidelines%20for%20Managem... accessed on 19th July 2022
