Bio- Medical Waste Management Rules, 2016 – Major Changes
DEFINITION of Bio Medical Waste
• “Bio-medical waste" means any waste, which is generated during the
• diagnosis,
• treatment or
• Immunization of human beings or
• Animals or research activities pertaining thereto or
• In the production or testing of biological or
• In health camps, including the categories mentioned in Schedule I appended to these rules
The New Rules are more comprehensive in nature
It contains important features of BMW (M & H) Rules, 1998
Several new provisions have been added in the new Rules
These rules may be called the Bio-Medical Waste Management Rules, 2016.
Bio-medical Waste Management Rules 2016
• SCHEDULES- 1 to 4
• FORMS- 1 to 5
• Rules – 1 to 18
Application
These rules shall apply to all persons who
– generate,
– collect,
– receive,
– store,
– transport,
– treat,
– dispose, or
– handle bio medical waste in any form
Include
– hospitals,
– nursing homes,
– clinics,
– dispensaries,
– veterinary institutions,
– animal houses,
– pathological laboratories,
– blood banks,
– Ayush hospitals,
– clinical establishments,
– research or educational institutions,
– health camps,
– medical or surgical camps,
– vaccination camps,
– blood donation camps,
– first aid rooms of schools,
– forensic laboratories and
– research labs
These Rules Shall Not Apply to:
a) Radioactive wastes as covered under the provisions of the atomic energy act, 1962(33 of 1962) and the rules made there under;
b) Hazardous chemicals covered under the manufacture, storage and import of hazardous chemicals rules, 1989 made under the act;
c) Solid wastes covered under the municipal solid waste (management and handling) rules, 2000 made under the act;
d) The lead acid batteries covered under the batteries (management and handling) rules, 2001 made under the act;
e) Hazardous wastes covered under the hazardous wastes (management, handling and transboundary movement) rules, 2008 made under the act;
f) Waste covered under the e-waste (management and handling) rules, 2011 made under the act; and
g) Hazardous micro organisms, genetically engineered micro organisms and cells covered under the manufacture, use, import, export and storage of hazardous microorganisms, genetically engineered micro organisms or cells rules, 1989 made under the Act.
Duties of Healthcare Facilities
• Initially:
– Every occupier of an institution generating bio-medical waste which includes a hospital, nursing home, clinic, dispensary, veterinary institution, animal house, pathological laboratory, blood bank to take all steps to ensure that such waste is handled without any adverse effect to human health and the environment
• Additions:
– pre-treat the laboratory waste, microbiological waste, blood samples and blood bags through disinfection or sterilization on-site
– in the manner as prescribed by WHO or NACO guidelines and then sent to the common bio-medical waste treatment facility for final disposal
– phase out use of chlorinated plastic bags, gloves and blood bags within two years from the date of notification of these rules
– provide training to all its health care workers and others involved in handling of bio medical waste at the time of induction and thereafter at least once every year
– immunize all its health care workers and others involved in handling of bio-medical waste for protection against diseases including Hepatitis B and Tetanus
– report major accidents including accidents caused by fire hazards, blasts during handling of bio-medical waste and the remedial action taken to SPCB
Treatment and Disposal of BMW
• Originally: Every HCFs, where required, shall set requisite bio-medical waste treatment facilities like incinerator, autoclave, microwave system for the treatment of waste, or, ensure requisite treatment of waste at a common waste treatment facility or any other waste treatment facility
• Change:
– No occupier shall establish on-site treatment and disposal facility, if a service of ` common bio- medical waste treatment facility is available at a distance of seventy-five kilometer
– In cases where service of the common bio-medical waste treatment facility is not available, the Occupiers shall set up requisite biomedical waste treatment equipment like incinerator, autoclave or microwave, shredder prior to commencement of its operation, as per the authorization given by the prescribed authority.
Segregation, packaging, transportation and storage
• Initially: Bio-medical waste classified in to 10 categories based on treatment options.
• Change:
– Bio-medical waste classified in to 4 categories based on treatment options.
– Aim is to improve the segregation of waste at source channelize proper treatment and disposal
• Initially: Hospitals treating 1000 or more patients per month to obtain authorization from SPCBs/PCCs
• Change:
– One time Authorization for Non-bedded HCFs.
– The validity of authorization shall be synchronized with validity of consent orders for Bedded HCFs
• Standards for emission from incinerators have been raised
– Duties have been fixed regarding the Site for common bio-medical waste treatment and disposal facility
– Allotment of land for CBWTF
– Reviewing the implementation of the Act
– Inspection of the facility
– Monitoring committees at
• District
• State and
• Central level
Act has 4 Schedules
• SCHEDULE I
– Biomedical wastes categories and their segregation, collection, treatment, processing and disposal options
– SCHEDULE II
– Standards for treatment and disposal of bio-medical wastes
– Schedule III
– List of Prescribed Authorities and the Corresponding Duties
– SCHEDULE IV
– Part A: label for bio-medical waste containers or bags
– Part B: label for transporting bio-medical waste bags or containers
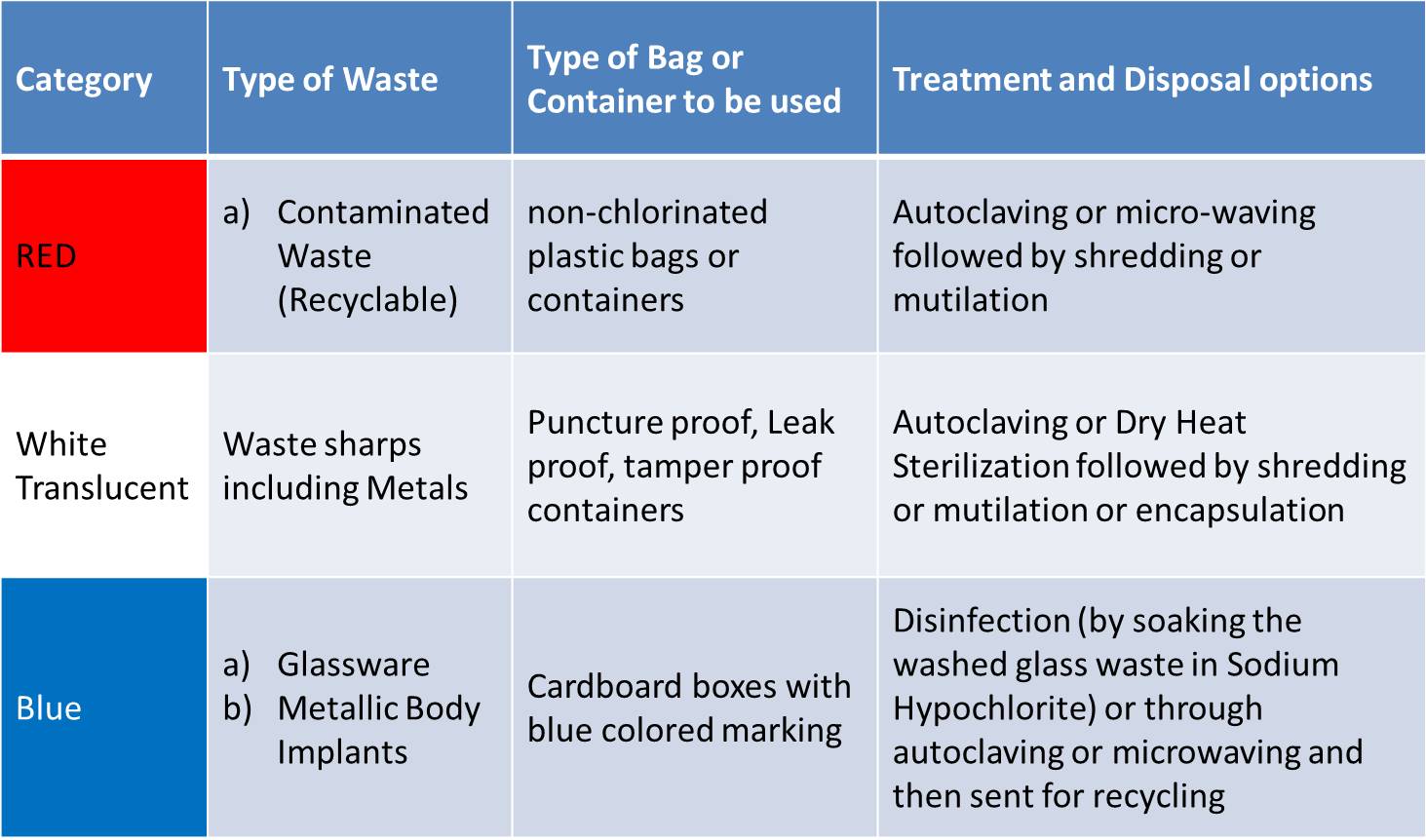
SCHEDULE I:
Biomedical wastes categories and their segregation, collection, treatment, processing and disposal options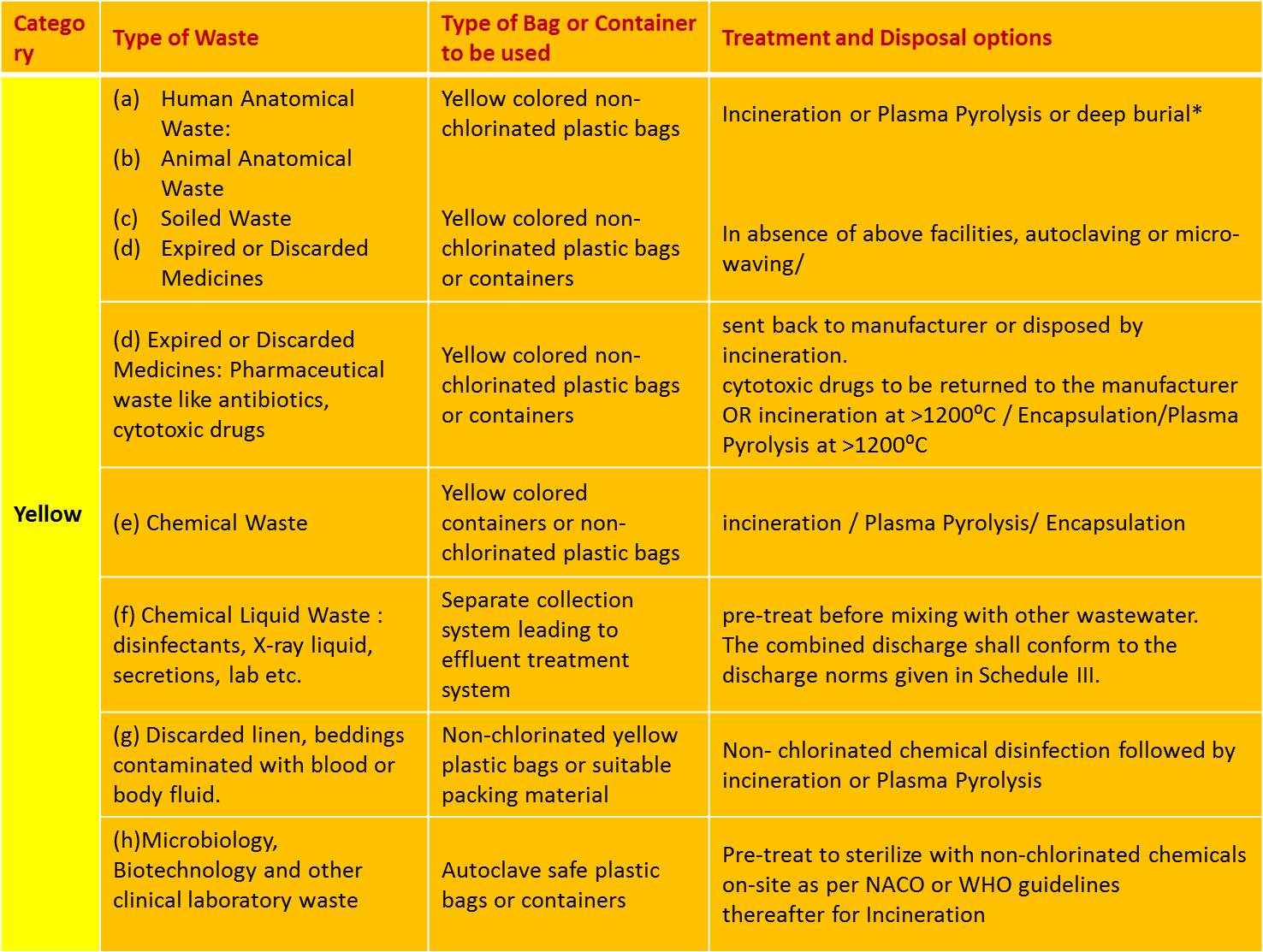
SCHEDULE II
Standards for treatment and disposal of bio-medical wastes
• STANDARDS FOR INCINERATION
– Operating Standards
– Emission Standards
• Operating and Emission Standards for Disposal by Plasma Pyrolysis or Gasification
– Air Emission Standards and
– Air Pollution Control Measures
– Disposal of Ash Vitrified Material
• Standards for autoclaving of bio-medical waste
• Standards of microwaving
• Standards for deep burial
• Standards for efficacy of chemical disinfection
• Standards for dry heat sterilization
• Standards for liquid waste
Schedule III
List of Prescribed Authorities and the Corresponding Duties
• This schedule lists the duties of the concerned administration e.g. making policies, issuing guidelines, inspection of premises, allocation of land, giving permission etc.
– Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Government of India
– Central or State Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Central Ministry for Animal Husbandry and Veterinary or State Department of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary.
– Central Pollution Control Board
– State Government of Health or Union Territory Government or Administration
– State Pollution Control Boards or Pollution Control Committees
– Municipalities or Corporations, Urban Local Bodies and Gram Panchayats
SCHEDULE IV
• Part A: label for bio-medical waste containers or bags

• Part B: label for transporting bio-medical waste bags or containers
– These are forms in which information is entered regarding
• Category
• Sender’s name
• Contact person etc.
Reference
• http://www.iaohindia.com/images/208/Major_Changes_in_BMW2016_implication...
• http://mpcb.gov.in/biomedical/pdf/BMW_Rules_2016.pdf
