
Essential elements:
• rehydration therapy,
• zinc supplementation, and
• continued feeding
Rehydration
Assess the hydration status as per the table below: (classify as no, some or severe dehydration present)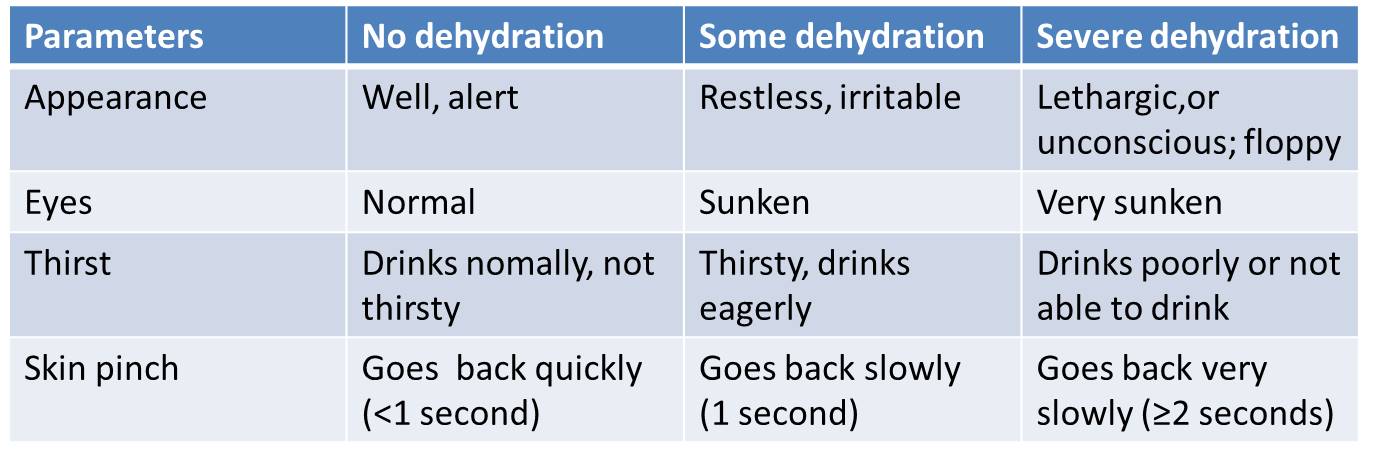
Rehydration in case of severe dehydration
• Rapid IV rehydration – followed by oral rehydration therapy
• Ringer’s lactate (RL) (a.k.a Hartmann’s solution) is recommended.
• If RL is not available, normal saline can be used
• Recommended amount is 100ml/kg of fluid: the rate of iv administration should be decided by the age of the child as given below:
aRepeat if the radial pulse is still very weak or not detectable
Rehydration in case of SOME dehydration:
• In the first 4 hours, give the child the following approximate amounts of ORS solution, according to the child’s weight (or age if the weight is not known), as shown in the chart below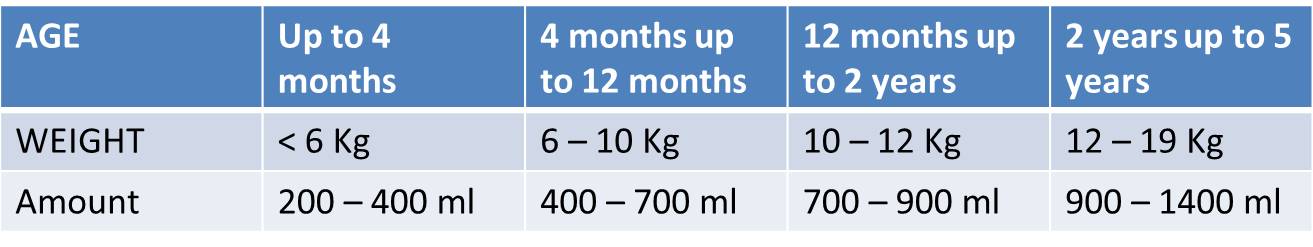
• Remember, if the child wants more to drink, he/she should be given more
• Demonstrate the mother how to give the ORS solution,
• One teaspoonful every 1–2 minutes if the child is under 2 years
• Frequent sips from a cup for an older child.
• If the child vomits, wait 10 minutes; then, resume giving ORS solution more slowly (e.g. a spoonful every 2–3 minutes).
• If the child’s eyelids become puffy, stop ORS solution and give plain water or breast milk.
• Advise breastfeeding mothers to continue to breastfeed whenever the child wants.
Reassess the child after 4 hours, checking for signs of dehydration. (Important: Reassess the child before 4 hours if the child is not taking the ORS solution or seems to be getting worse.) —
• If there is no dehydration, teach the mother the four rules of home treatment
• If still there is SOME DEHYDRATION, repeat the above treatment
4 rules of home treatment are:
1. Give extra fluid
2. Give zinc supplements for 10 – 14 days
3. Continue feeding
4. Teach her when to return
In case of NO dehydration
• Recommend extra fluids at home to prevent dehydration.
• Explain the mother that it is important that the child needs to receive an appropriate diet for their age, including continued breastfeeding.
• Explain the 4 rules of home treatment
• If the mother cannot stay for 4 hours, show her how to prepare ORS solution and give her enough ORS packets to complete the rehydration at home plus enough for 2 more days.
Antibiotics should NOT be used routinely.
Antibiotics should be considered in cases of:
• bloody diarrhoea (probable shigellosis),
• suspected cholera with severe dehydration, and
• Serious parenteral infections such as pneumonia.
Antiprotozoal drugs are rarely indicated.
CAUTION:
“Antidiarrhoeal” drugs and anti-emetics should not be given to young children with acute or persistent diarrhoea (or dysentery):
• they do NOT prevent dehydration or
• they do NOT improve nutritional status and
• some have dangerous, sometimes fatal, side-effects
Reference:
• WHO, 2005 : Pocket Book of Hospital Care for Children; GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF COMMON ILLNESSES WITH LIMITED RESOURCES; available on file:///C:/Users/Lenovo/Documents/books/child%20care/WHO%20child%20mgmt%20module.pdf accessed on 19 July 2016
Clinical features suggestive of dehydration: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/clinical-features-suggestive-dehydration
ORAL REHYDRATION SALT (ORS): http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/oral-rehydration-salt-ors
Management of Acute Diarrhoea in Children: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/management-acute-diarrhoea-children
4 Rules of Home Treatment for Diarrhea in Children: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/4-rules-home-treatment-diarrhea-children
Sugar Salt Solution for Rehydration: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/sugar-salt-solution-rehydration
6 Steps of ‘Skin Pinch’ Test for Assessing Dehydration: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/6-steps-%E2%80%98skin-pinch%E2%80%99-test-a...
Some Clinical features of diarrhea due to common causative organisms: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/some-clinical-features-diarrhea-due-common-...
Principles of management of diarrhea: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/principles-management-diarrhea
Control of diarrheal diseases: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/control-diarrheal-diseases
Indicators of Diarrhea Control: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/indicators-diarrhea-control
Vaccines for prevention of diarrhea: http://www.ihatepsm.com/blog/vaccines-prevention-diarrhea
Lecture on acute diarrheal disaeses-1 (epidemiology): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8VMSn7mJgm8&t=215s
Lecture on acute diarrheal disaeses-2 (control): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=85iOg3GNevU&t=41s
Lecture (HINDI) on acute diarrheal disaeses-1 (epidemiology): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c-bOaC55u-g&t=5s
Lecture (HINDI) on acute diarrheal disaeses-2 (control): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=acc-nqkjar4&t=1s
